In order to obtain detailed images from an ultrasound system, the ultrasound used must be very high-pitched, i.e. at very high frequencies between 3 and 20 MHz. However, at such frequencies, ultrasound is no longer transmitted through the air. Therefore, a substance capable of expelling air between the transducer and the patient’s skin must be used. This is why, as we saw in question 3, an ultrasound system can’t help in the study of organs that contain a lot of air.
Using an ultrasound gel allows ultrasound to be transmitted without modifying it. Pure water could also be used in the same way, but a gel is more practical because it doesn’t leak, doesn’t get the patient wet, serves as a lubricant and seals the roughness between the transducer and the skin. During certain procedures, a disinfectant such as povidone-iodine can be used instead.
Ultrasound gel, which is applied generously to the belly of a pregnant woman for a prenatal ultrasound, for example, is composed of purified water, a gelling agent and preservatives (antibacterial). In general, it is neither greasy nor tinted and does not leave any stains or marks on the patient’s clothing. It is not advisable to warm it up because a warmer temperature will reduce its cohesiveness and promote the development of germs.


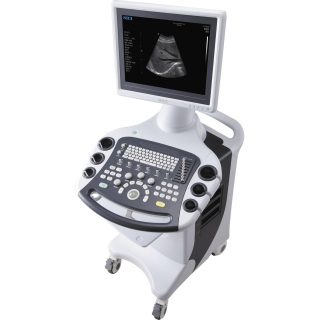



I totally agree that medical practitioners should consider the size of the screen for an ultrasound machine as well as taking into consideration the quality of image that it produces because it is imperative for many diagnostics. I remember when I took my wife for her antenatal check-up and we were very pleased to know that the maternity hospital is equipped with an ultrasound machine that can display up to 250 shades of grey. I do believe that medical practitioners should take this into consideration when buying and ultrasound machine.