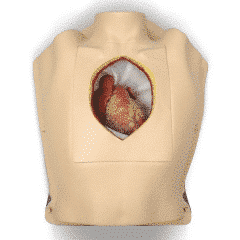
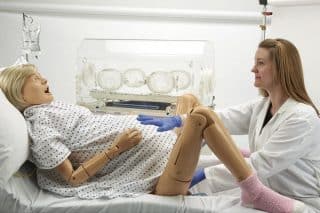
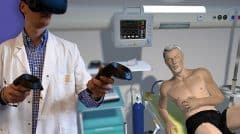
In the medical field, simulations provide an immersive, hands-on learning experience in a safe environment that does not compromise patient safety. Medical simulations can be performed on either real people who play the role of patients or on medical devices. This guide focuses mainly on medical devices, such as various simulators and training manikins.
Simulators are devices used for training in various medical procedures. They are designed to represent all or part of the human (or animal, for veterinary purposes) body. They are usually equipped with an electronic system that recreates vital signs, movements, etc. They are often used in immersive medical practice environments.